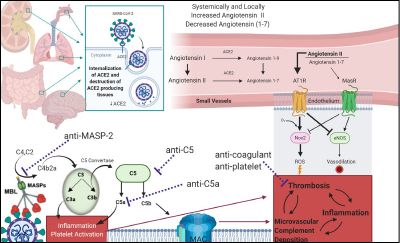
 | Model for AP and LP complement activation by SARS-CoV2, and its interaction with coagulation cascades |
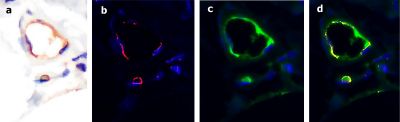 | Co-expression of ACE2 and SARS CoV-2 capsid proteins with the cutaneous and subcutaneous microvasculature in a normal deltoid skin biopsy from a patient with fatal COVID-19 associated ARDS. |
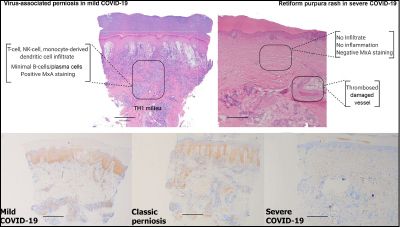
| Comparative light microscopic findings and myxovirus resistance protein A (MXA) pattern of immunoreactivity in COVID-19-associated perniosis, idiopathic perniosis and COVID-19-associated thrombotic retiform purpura. |
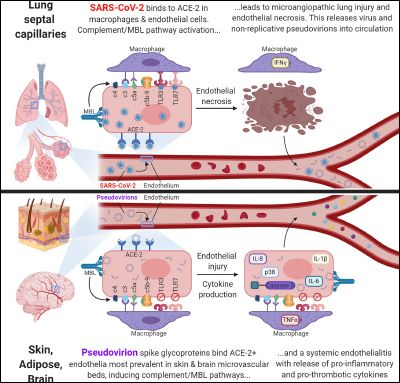 | Severe COVID-19: A multifaceted viral vasculopathy syndrome Graphic representation of the two distinct mechanisms of severe COVID-19. |
Livedoid and Purpuric Skin Eruptions Associated With Coagulopathy in Severe COVID-19
Anti-complement C5 therapy with eculizumab in three cases of critical COVID-19
Concomitant calciphylaxis and COVID-19 associated thrombotic retiform purpura
A Covid-19 Patient with Complement-Mediated Coagulopathy and Severe Thrombosis